Self Service Automation: How to Empower Your Business
Self service automation can help break down organizational silos to boost employee efficiency. Check out these best practices to help your help desk reduce the burden of routine business requests.

To keep the business running smoothly, IT Ops teams collaborate with a variety of stakeholders, from software developers and security teams to business leaders and customer support. But with so many groups and individuals involved, it’s easy for things to fall through the cracks, leading to delays, frustration, and even costly mistakes.
Fortunately, self-service automation empowers users across the business with access to a centralized automation platform. The platform itself is controlled and managed by the automation group. End users in other departments gain a secure and easy-to-use set of tools to support their departments. It's a win-win! Let’s look at how it can help break down your organizational silos.
What is Self-Service Automation?
Self-service automation allows users to not only trigger business processes, but cancel and restart those jobs as well. Many self-service applications also provide monitoring so users can follow job progress. To achieve this, end-users may access web-based applications with intuitive user interfaces or the business-productivity tools they use in day-to-day business.
Now more than ever, business users expect — and prefer — self-service automation to get what they need, when they need it. This has the dual benefit of enhancing user experience and customer satisfaction while reducing the workload on IT.
The Rise of Automation for Everyone
Historically, IT automation access has been limited to and controlled by IT operations teams. Today, IT Ops can’t scale to meet the demand for automation across the business on their own. As a result, they’re delivering automation as a service to let end-users trigger, check, and build their own workflows.
According to the 2025 Global State of IT Automation report, 92% of respondents offer self-service automation to their organizations. Additionally, 63% said they have 200+ end-users.
This explosive growth in citizen automators across all functions indicates that self-service is rapidly becoming a mainstream approach.
Shift Toward Empowering Non-Ops Teams
There is a significant shift toward empowering teams outside of IT Ops. The same Global State of IT Automation report shows that 92% of respondents allow end-users to do their own workflows, tools, and processes. In fact, IT Ops is empowering employees with centrally controlled self-service automation portals to increase speed and agility.
End-users include IT Ops, data, cloud, development, and line-of-business teams. User growth has been especially strong in ITOps, data teams, and line of business. Each have experienced over 20% year over year growth in volume of end users.
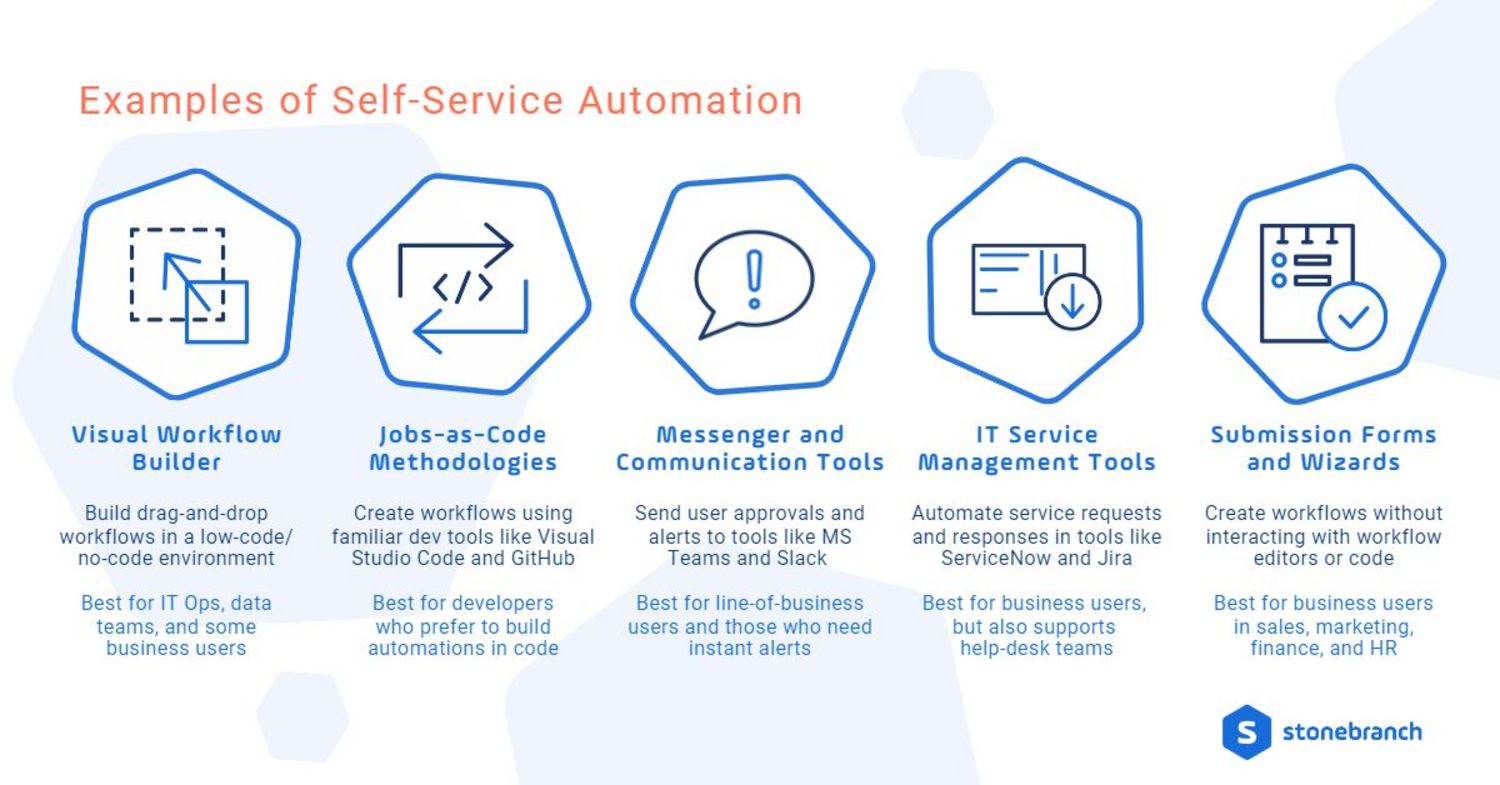
Examples of Self Service Automation
Implementing a self-service automation portal isn't the only way to deliver an automated service solution to your organization. Different employees require different ways to interact and use automation as a service. Examples of best practices in self-service automation include:
- Visual workflow builder to build drag-and-drop workflows in a low-code/no-code user interface.
Best suited for: IT Operations, Data Teams, and some business users. - Jobs-as-code to create workflows using familiar development tools like Visual Studio Code. Developers typically pair jobs-as-code with code repositories, like GitHub, to promote code and collaborate with other team members.
Best suited for developers who prefer to write code. - Messenger and communication tools that integrate with automation platforms enable users to trigger workflows, approve jobs, get alerts when something goes wrong, etc.
Best suited for line-of-business users but is also helpful for any discipline that needs instant alerts. - ITSM tools, like ServiceNow or Jira, that integrate with automation platforms allow end-users to trigger automated workflows from within their service request catalog. Additionally, automation platforms should be able to open tickets when a job or workflow goes down.
Best suited for business users, with additional benefits for help-desk teams. - Self-Service Portals allow non-technical users to check, trigger, and review automation without interacting with any code or complex screens. These simplified end-user experiences are often available on multiple devices, including mobile, to help with anytime and anywhere access. Visit the Universal Portal to get a sense of the features a self-service portal can offer.
Best suited for business users who don’t want or don’t have the technical ability to create automation. Best suited for line-of-business users, including sales, marketing, finance, and HR.
Implementing Best Practices
Self-service solutions allow people in an organization to execute tasks and workflows without being dependent on IT. This helps people control their own processes, reduces repetitive manual work, enhances security and compliance, and boosts efficiency — for the end-user and the IT service management team.
Below are automation examples that are applied by different teams and individuals across a typical enterprise.
Data Pipeline Orchestration
Automation helps DataOps teams orchestrate the data flow between source, ETL, storage, and reporting tools along a data pipeline. Automated processes can quickly retrieve, transfer, and update data in real-time without human intervention.
Software Deployment
For DevOps teams, automated software deployment eliminates manual installation and configuration. This saves time and eliminates human error, ensuring that software deploys consistently and accurately every time.
Infrastructure Management
Automated infrastructure management empowers non-IT staff to turn cloud infrastructure on and off — while IT Ops maintains central control and visibility. Pre-defined templates and workflows automate the management of the entire infrastructure lifecycle, including shutting down infrastructure to reduce sprawl.
Service Desk Support
Many requests that come through the help desk can be easily automated without negatively impacting customer experience service levels. These days, business users expect self-service technology for password resets, employee onboarding, and even basic computer troubleshooting. Organizations can reduce the volume of service requests by using self-service tools. Doing so frees up admins to tackle more complex technical issues.
Business Productivity
Non-technical employees often aren't aware of the productivity gains that can be achieved by streamlining processes and automating workflows. Automation can free up personnel in functions such as marketing, finance, and HR to focus on more creative or strategic tasks.
Ultimately, self-service reduces the burden on IT teams, while it empowers the rest of the organization to move at their own speed to get the answers they need.
Benefits of Empowering Teams with Automation
Business processes typically span multiple automation tools and system integrations that require central orchestration. A centralized workload automation platform can help bring these people, platforms, and processes together to enable enterprise-wide:
- Collaboration: cross-functional synergies can be achieved by centralizing automation efforts on a platform that easily integrates with any of the tools or systems your organization uses — now and in the future.
- Observability: with a platform approach to automation, the central IT team gains the ability to monitor and put guardrails in place for the rest of the organization. This guidance empowers end-users to make and monitor their own workflows.
- Productivity: Automation is a game changer for end-users that have not traditionally had access. Having access to automation creates opportunities to find new efficiencies and drive innovations that weren’t possible with manual tasks.
- Eliminate Shadow Automation: It's so easy for employees to spin up rogue open-source or cloud automation tools. Unfortunately, this behavior creates security, governance, and efficiency blind spots for the IT Ops team. By offering a platform that's both accessible and user-friendly, IT Ops maintains control and visibility.
Next Steps
Are you ready to unlock organizational efficiency? Check out this video to see how ING Group empowers end-users with self-service automation.
Frequently Asked Questions: Automated Self-Service
What is self-service automation?
Self-service automation empowers users throughout the organization to set up, trigger, stop, restart, and monitor business processes. End-users perform tasks on their own using digital tools, without the need for human intervention.
How can automation applications provide monitoring?
Usually, automation applications offer a web-based interface that's user-friendly and easy to navigate. Users can keep tabs on their tasks and operations in real-time and quickly identify potential bottlenecks.
What are some best practices in self-service automation?
To start, identify the most labor-intensive processes in your organization, then work with the teams involved to create a plan for automation. Provide users with the necessary tools for independent work. Continuously monitor and improve automation processes.
Can self-service automation reduce the need to hire new employees?
Service desk teams play a crucial role in automation. They provide support and facilitate adoption during the initial implementation. Business teams rely on their expertise for user guidance, training, and troubleshooting. The service desk is also often responsible for managing and continuously improving the self-service catalog.
What are some examples of self-service automation?
Examples of self-service automation solutions include visual workflow builders, jobs-as-code methodologies, messenger and communication tool integrations, ITSM integrations, as well as front-end job submission forms or wizards.
What is the role of the service desk in self-service automation?
Yes, automation may reduce the need to hire new employees in certain areas of your business. By automating routine tasks and processes, you can free up your current employees to focus on more strategic activities that require human creativity and ingenuity. When it's time to grow your team, automate the onboarding process to bring new hires up to speed quickly and efficiently.
How can business partners benefit from automated self-service?
Business partners can benefit from self-service by gaining role-appropriate access to the same digital tools and processes used by your IT Ops team. This can help to streamline communication and collaboration, and improve the overall efficiency of your business processes.
How can self-service automation be used to reduce waiting times?
You can use self-service to reduce waiting times for routine tasks and processes that were previously handled by human employees. This can help to improve the overall customer experience and increase satisfaction with your products and services.
Start Your Automation Initiative Now
Schedule a Live Demo with a Stonebranch Solution Expert




